| Background |
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) stimulates the acute phase of the immune response. In response to a pathogen, TNF alpha is one of the first to be released and can apply its effects in many organs. TNF alpha stimulates the release of corticotropic releasing hormone, suppresses appetite, and induces fever, in the hypothalamus. TNF increase vasodilation and loss of vascular permeability, it helps recruit lymphocyte, neutrophil, and monocyte to the inflammation site by regulating chemokine release. |
| Synonyms |
tumor necrosis factor beta, TNFSF1B, Lymphotoxin-alpha (LT-α),LTA |
| Uniprot ID |
P01375 |
| Molecular Weight |
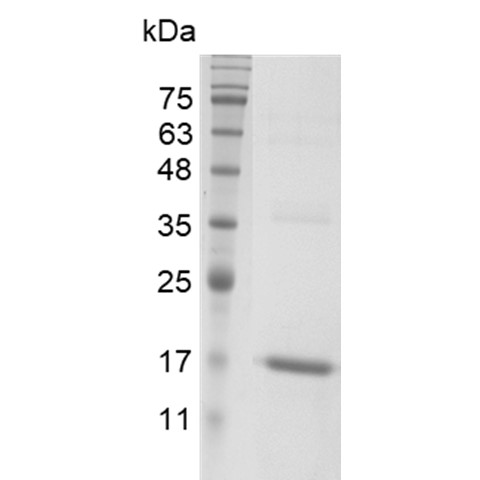
The protein has a calculated MW of 18.3 kDa.
The protein migrates as 17 kDa under reducing condition (SDS-PAGE analysis). |
| Expression System |
Escherichia coli |
| Purity |
>97% as determined by SDS-PAGE analysis. |
| Activity |
Measure by its ability to induce cytotoxicity in L929 cells in the presence of actinomycin D. The ED₅₀ for this effect is < 0.1 ng/mL. The specific activity of recombinant human TNF alpha is approximately ≧ 1 x 10⁷ IU/mg, which is calibrated against the human TNF Alpha WHO International Standard (NIBSC code: 12/154). |
| Endotoxin Level |
<0.05 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method. |
| Protein Sequence |
MVRSSSRTPSDKPVAHVVANPQAEGQLQWLNRRANALLANGVELRDNQLVVPSEGLYLIYSQVLFKGQGCPSTHVLLTHTISRIAVSYQTKVNLLSAIKSPCQRETPEGAEAKPWYEPIYLGGVFQLEKGDRLSAEINRPDYLDFAESGQVYFGIIAL with polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Protein Tag |
His Tag (C-term) |
| Form |
Lyophilized from a 0.2 µm filtered solution of PBS, pH 8.0. |
| Application |
Cell Culture |
 No references are available
No references are available
 Follow Us
Follow Us