| Background |
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) was first identified as a growth factor due to its ability to induce proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow progenitors into granulocytes and macrophages. GM-CSF is produced by multiple cell types including activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, endothelial cells and fibroblasts upon receiving immune stimuli. GM-CSF stimulates stem cells to produce granulocytes and monocytes functions as a cytokine. |
| Synonyms |
granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, colony stimulating factor 2, CSF2, CSF-2 |
| Uniprot ID |
P04141 |
| Molecular Weight |
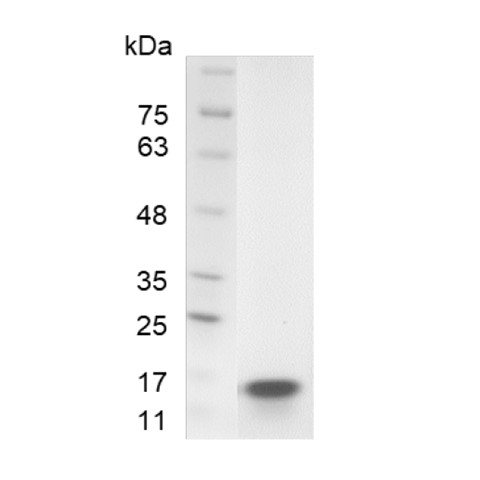
The protein has a calculated MW of 15.4 kDa.
The protein migrates as 15 kDa under reducing condition (SDS-PAGE analysis). |
| Expression System |
Escherichia coli |
| Purity |
>98% as determined by SDS-PAGE analysis. |
| Activity |
Measure by its ability to induce TF-1 cells proliferation. The ED₅₀ for this effect is <80 pg/mL. The specific activity of recombinant human GM-CSF is approximately >1 x 10⁷ IU/mg. |
| Endotoxin Level |
<0.05 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method. |
| Protein Sequence |
APARSPSPSTQPWEHVNAIQEARRLLNLSRDTAAEMNETVEVISEMFDLQEPTCLQTRLELYKQGLRGSLTKLKGPLTMMASHYKQHCPPTPETSCATQIITFESFKENLKDFLLVIPFDCWEPVQE with polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Protein Tag |
His Tag (N-term) |
| Form |
Lyophilized from a 0.2 µm filtered solution of PBS, pH 8.0. |
| Application |
Cell Culture |
 No references are available
No references are available
 Follow Us
Follow Us