| Background |
Human epidermal growth factor (EGF) is a 6 kDa cytokine with 53 amino acid residues. EGF is mainly secreted from ectodermal cells, monocytes, kidney and duodenal glands. Upon binding to its receptor, EGFR, EGF acts to stimulate cell growth and proliferation of epithelial cells, play important roles in many developmental processes including accelerate tooth eruption, inhibits gastric acid secretion, and involve in wound healing. |
| Synonyms |
epidermal growth factor, Urogastrone, URG |
| Uniprot ID |
P01133 |
| Molecular Weight |
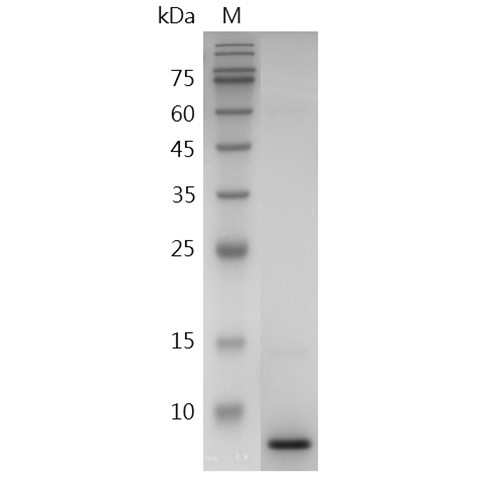
The protein has a calculated MW of 7.16 kDa.
The protein migrates as 9-11 kDa under reducing condition (SDS-PAGE analysis). |
| Expression System |
Escherichia coli |
| Purity |
>97% as determined by SDS-PAGE analysis. |
| Activity |
Measure by its ability to induce 3T3 cells proliferation. The ED₅₀ for this effect is <1.0 ng/mL. The specific activity of recombinant human EGF is approximately >1.0 x 10⁶ IU/mg. |
| Endotoxin Level |
<0.05 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method. |
| Protein Sequence |
MNSDSECPLSHDGYCLHDGVCMYIEALDKYACNCVVGYIGERCQYRDLKWWELR with polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus |
| Protein Tag |
His Tag (C-term) |
| Form |
Lyophilized from a 0.2 µm filtered solution of PBS, pH 8.0. |
| Application |
Cell Culture |
 No references are available
No references are available
 Follow Us
Follow Us