| Background |
GFAP (Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein) is a protein primarily found in CNS astrocytes. Increased GFAP immunoreactivity indicates gliosis, a response to neural damage. GFAP defects cause Alexander disease, a rare CNS disorder with astrocytic Rosenthal fiber accumulation. The infantile form leads to myelination failure and early mortality, while the juvenile or adult forms present with ataxia, bulbar signs, spasticity, progressing more gradually. |
| Synonyms |
Glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| Uniprot ID |
P14136 |
| Molecular Weight |
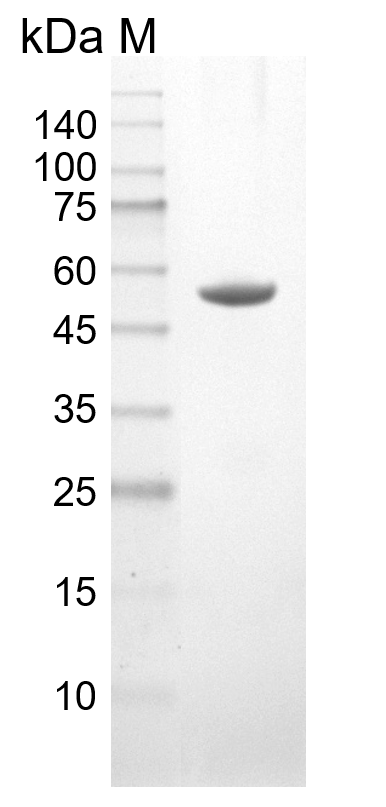
The protein has a calculated MW of 51 kDa.
The protein migrates as 50-55 kDa under reducing condition (SDS-PAGE analysis). |
| Expression System |
Escherichia coli |
| Purity |
>98% as determined by SDS-PAGE analysis. |
| Activity |
Testing in process |
| Endotoxin Level |
<0.1 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method. |
| Protein Sequence |
A DNA sequence encoding Human GFAP Protein (#P14136)(Met1-Met432) was expressed with polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Protein Tag |
His Tag (C-term) |
| Form |
The protein was lyophilized from a 0.2 µm filtered solution containing 1X PBS, pH 7.4. If you have any concerns or special requirements, please confirm with us. |
| Application |
Cell Culture |

 No references are available
No references are available
 Follow Us
Follow Us