| Background |
Basic fibroblast Growth Factors (FGF-2, bFGF), a pleiotropic cytokine, plays multiple roles in different cells and tissues. FGF-2 can stimulate smooth muscle cell growth, wound healing, and tissue repair. In addition, FGF-2 has been shown to regulate the generation of neurons and astrocytes from progenitor cells. FGF-2 are also involved in a variety of biological processes, including embryonic development, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth, and invasion. As a multifunctional cytokine, FGF-2 is first isolated from the pituitary. Later, it was identified from various cell types including cardiac myocytes, cardiac fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells. |
| Synonyms |
fibroblast growth factor 2, Fgfb, bFGF, FGF-basic |
| Uniprot ID |
NP_001392443 |
| Molecular Weight |
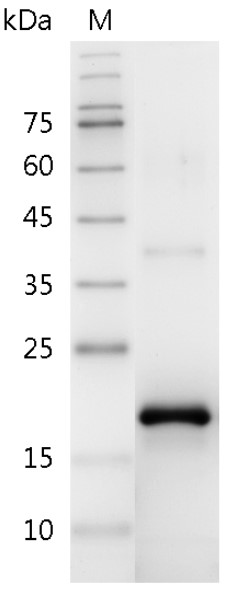
The protein has a calculated MW of 18.1 kDa.
The protein migrates as 17 kDa under reducing condition (SDS-PAGE analysis). |
| Expression System |
Escherichia coli |
| Purity |
>98% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Activity |
Measure by its ability to induce proliferation in 3T3 cells.
The ED₅₀ for this effect is <2 ng/mL. |
| Endotoxin Level |
<0.1 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method. |
| Protein Sequence |
AAGSITTLPALPEDGGSGAFPPGHFKDPKRLYCKNGGFFLRIHPDGRVDGVREKSDPHIKLQLQAEERGVVSIKGVCANRYLAMKEDGRLLASKCVTDECFFFERLESNNYNTYRSRKYSSWYVALKRTGQYKLGPKTGPGQKAILFLPMSAKS with polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Protein Tag |
His Tag (N-term) |
| Form |
The protein was lyophilized from a 0.2 µm filtered solution containing 0.01% sarkosyl in 1X PBS, pH 7.4. If you have any concerns or special requirements, please confirm with us. |
| Application |
Cell Culture |
 No references are available
No references are available
 Follow Us
Follow Us